Archives
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
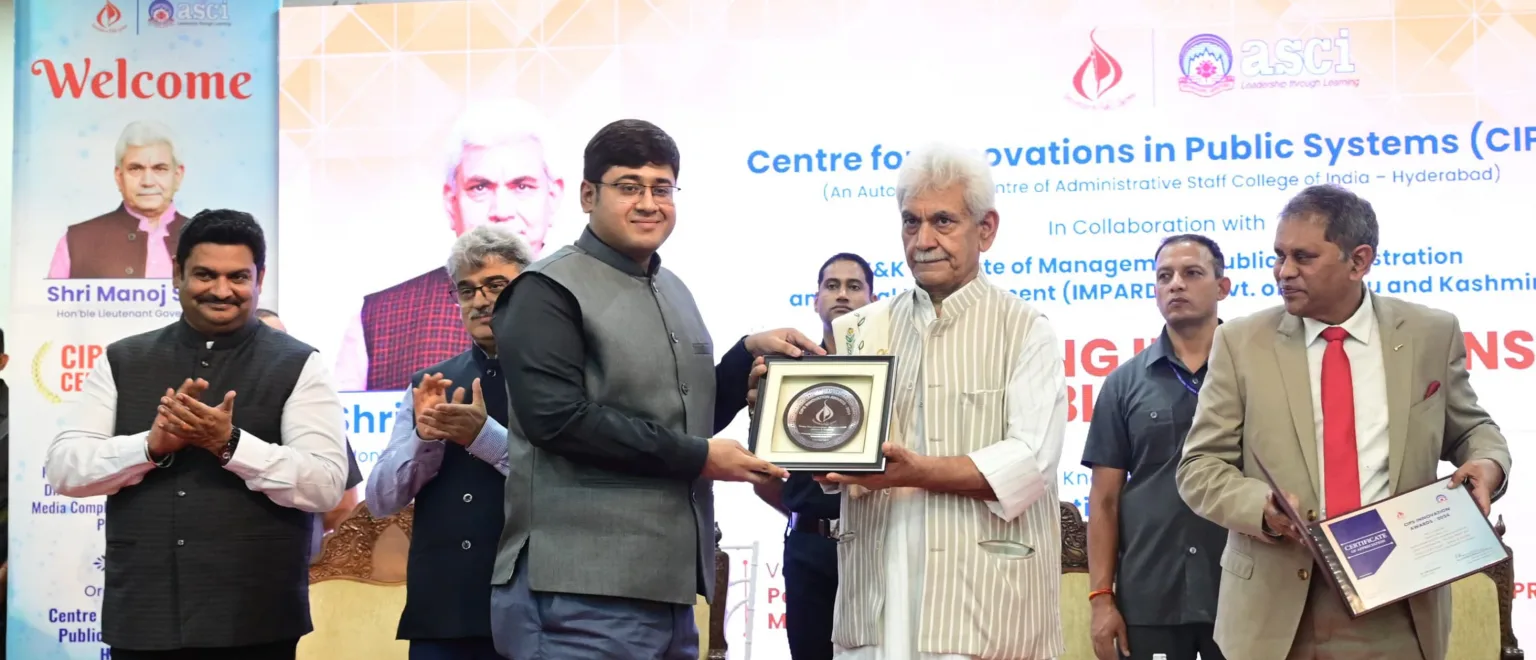
LG Sinha felicitates CIPS Award Winners in Srinagar, calls for Innovation in Governance
Lieutenant Governor Manoj Sinha on Friday felicitated the winners of the Centre for Innovations in Public Systems (CIPS) Awards at a ceremony held in Srinagar. The CIPS awards recognize and…
Crackdown on terror ecosystem: LG terminates services of two J&K govt employees
Srinagar, Aug 22: Lieutenant Governor Manoj Sinha on Friday terminated the services of two government employees in the Union Territory over their alleged involvement in terror activities, officials said. The sacked…
Dr Singh to inaugurate two high-tech innovation centres at IUST
Awantipora, Aug 22: In a major boost to innovation and entrepreneurship in…
Budgam: Khag residents demand degree college
Students cite difficulties in travelling to Beerwah, Magam colleges
Salman Khan starts shooting for ‘Battle of Galwan’ in Ladakh
Leh, Aug 22: Bollywood superstar Salman Khan has officially commenced shooting for…
Govt sanctions state-of-the-art oxygen generation plant for GMC Anantnag
Srinagar, Aug 22: The Health and Medical Education Department on Friday sanctioned…
JKAS 2025 NOTIFICATION OUT: J&K Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination 2025
Applications, through online mode, are invited from applicants, who are domiciled in…
IMD Regional Centre in Jammu soon: Dr Jitendra
- Union Minister says National Mission launched for Himalayan ecosystem sustainability -…
56th Raising Day : CM Omar inaugurates girls’ hostel ‘Triveni’ at Sainik School Nagrota
Jammu, Aug 22: Sainik School Nagrota marked its 56th Raising Day with…
DC Jammu calls for strengthening basic school infrastructure
Jammu, Aug 22: Deputy Commissioner Jammu Dr Rakesh Minhas on Friday called…
Himalayas on the Edge: J&K, Ladakh hit by worsening climate extremes, glacial threats
•Report projects doubling of heatwaves, 43% surge in extreme rainfall by 2030
ISRO’s Roadmap for Viksit Bharat 2047
Indian Space Research is entering into a new era that will define the nation’s roadmap for Viksit Bharat 2047.This was…
Sports
J&K Assembly session likely in Sept, says Minister Dar
Srinagar, Aug 22: Cabinet Minister Javid Dar on Friday said the Assembly…