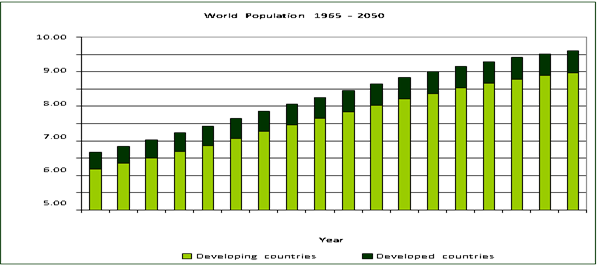
By embracing precision agriculture, vertical farming, genetic engineering, synthetic biology, blockchain, and the entrepreneurial drive of AgriTech startups, we can create a food system capable of sustaining 9.1 billion people by 2050
FEEDING THE FUTURE
As the global population is projected to reach 9.1 billion by 2050, the challenge of ensuring food security looms large. Traditional agricultural practices alone will not suffice to meet the growing demand for food. Fortunately, a wave of innovative technologies is emerging, promising to revolutionize food production and create a sustainable future. Here, we explore the cutting-edge advancements poised to transform agriculture and ensure a bountiful harvest for generations to come.
Precision Agriculture: The Power of Data and Automation
Precision agriculture is at the forefront of the agricultural revolution, leveraging data and automation to optimize farming practices. Utilizing GPS technology, remote sensing, and IoT devices, precision agriculture enables farmers to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns with unprecedented accuracy. By collecting and analyzing data in real-time, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, reducing resource wastage and increasing crop yields. Automated machinery, such as drones and autonomous tractors, further enhances efficiency by performing tasks like planting, spraying, and harvesting with pinpoint precision. This technology not only maximizes productivity but also minimizes environmental impact, promoting sustainable farming practices.
Vertical Farming: Growing Upwards for Urban Food Security
As urbanization continues to expand, vertical farming offers a promising solution to food security in densely populated areas. Vertical farms utilize stacked layers of crops grown in controlled environments, such as warehouses or skyscrapers, using hydroponic or aeroponic systems. By cultivating crops indoors, vertical farms eliminate the need for large tracts of arable land and reduce transportation costs and emissions associated with food distribution. These farms can operate year-round, regardless of weather conditions, and use significantly less water than traditional agriculture. LED lighting and climate control systems ensure optimal growing conditions, resulting in higher yields and faster growth cycles. Vertical farming is poised to bring fresh, locally-grown produce to urban centers, reducing dependency on distant agricultural regions.
CRISPR and Genetic Engineering: Tailoring Crops for Resilience
Advances in genetic engineering, particularly CRISPR technology, are revolutionizing crop development. CRISPR allows scientists to precisely edit the DNA of plants, introducing traits that enhance their resilience to pests, diseases, and extreme weather conditions. Crops can be engineered to grow in adverse conditions, such as drought-prone or saline soils, expanding the potential for agriculture in previously inhospitable regions. Additionally, genetic modifications can improve the nutritional content of crops, addressing malnutrition and enhancing food quality. By creating crops that are more resilient and nutritious, genetic engineering holds the key to sustaining agricultural productivity in the face of climate change and increasing global demand.
Synthetic Biology: Creating Novel Food Sources
Synthetic biology is opening new frontiers in food production by designing and constructing novel biological systems. One of the most exciting applications is the development of lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat or cellular agriculture. Lab-grown meat is produced by culturing animal cells in bioreactors, eliminating the need for traditional livestock farming. This technology promises to address the environmental and ethical concerns associated with conventional meat production, such as greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and animal welfare. As the technology matures and scales up, lab-grown meat could become a sustainable and efficient source of protein, reducing the strain on natural resources.
Blockchain Technology: Ensuring Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology is set to revolutionize the agricultural supply chain by providing transparency and traceability from farm to table. By recording every transaction on a decentralized ledger, blockchain ensures the authenticity and safety of food products, combating fraud and contamination. Farmers can use blockchain to track the journey of their produce, ensuring it reaches consumers in optimal condition. This technology also enables consumers to verify the origins and quality of their food, fostering trust and confidence in the food supply. Blockchain’s potential to streamline logistics and reduce food waste further contributes to a more sustainable and efficient agricultural system.
AgriTech Startups: Driving Innovation and Collaboration
A burgeoning ecosystem of AgriTech startups is driving innovation and collaboration in the agricultural sector. These startups are developing cutting-edge solutions, from AI-powered crop monitoring systems to biodegradable packaging made from agricultural waste. By partnering with farmers, research institutions, and governments, AgriTech startups are accelerating the adoption of new technologies and practices. Their entrepreneurial spirit and technological prowess are essential in tackling the multifaceted challenges of modern agriculture, ensuring a resilient and sustainable food system for the future.
The convergence of these innovative technologies marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of agriculture. By embracing precision agriculture, vertical farming, genetic engineering, synthetic biology, blockchain, and the entrepreneurial drive of AgriTech startups, we can create a food system capable of sustaining 9.1 billion people by 2050. The path to a food-secure future is paved with technological advancements that optimize resources, enhance crop resilience, and ensure transparency. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and population growth, these innovations will play a crucial role in cultivating a sustainable and abundant future for all.
(Author is Scientist- MRCFC-Khudwani, SKUAST-Kashmir. Visiting Scientist University of Nebraska Lincon, USA. Feedback: drahmadm786@rediffmail)
Box: The path to a food-secure future is paved with technological advancements that optimize resources, enhance crop resilience, and ensure transparency. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and population growth, these innovations will play a crucial role in cultivating a sustainable and abundant future for all