Archives
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
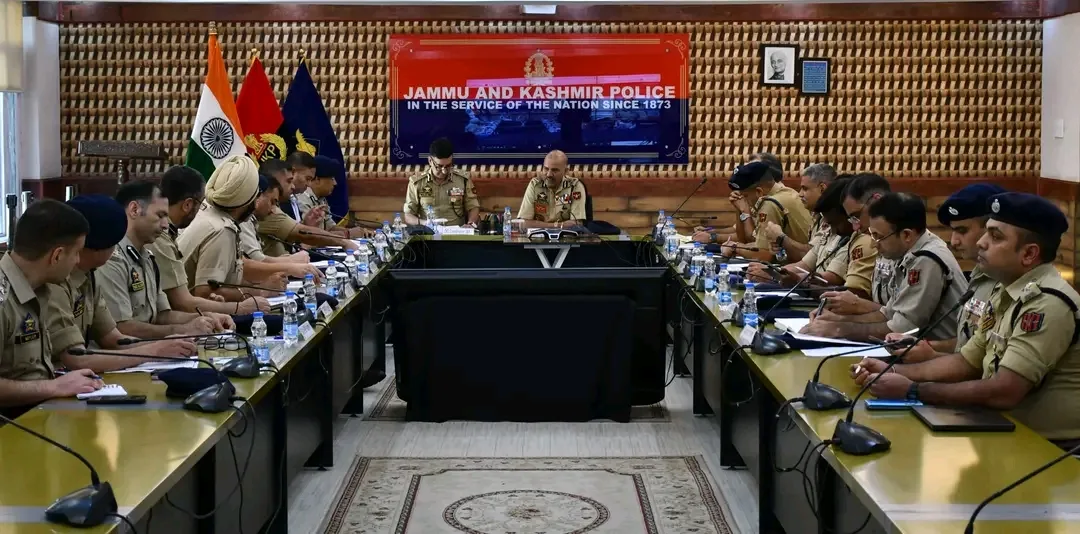
‘Ensure Foolproof Security, Monitor Social Media Closely’: DGP J&K to Officers
Director General of Police J&K, Nalin Prabhat-IPS chaired a security review meeting at the Conference Hall of Police Control Room Kashmir today, to assess the prevailing security situation in the…
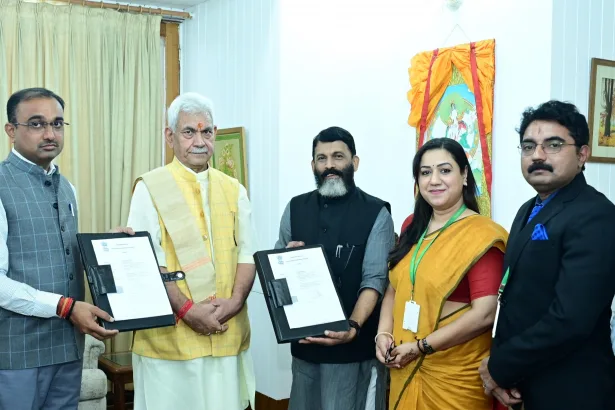
Historic Move: Free homes for families hit by terrorism & natural calamities: LG
Says smart housing is the first step toward long-term rehab in J&K
Supreme sacrifices of brave forest personnel will always be remembered: Rana
Pays glowing tributes to martyrs Says upcoming Ecotourism Park, other infra to…
Workshop on embedded systems & IOT held at IUST
Awantipora, Sept 11: A workshop on Embedded Systems and the Internet of…
Police organise medical camp on drug abuse
Anantnag, Sept 11: Under the aegis of Civic Action Programme-2025 and in…
‘Ensure Foolproof Security, Monitor Social Media Closely’: DGP J&K to Officers
Director General of Police J&K, Nalin Prabhat-IPS chaired a security review meeting…
DC reviews post-rainfall restoration measures in Bani sub-division
Distributes relief material among affected families
Krishi Udyamis complete Integrated Nutrient Management certificate course
Kishtwar, Sep 11: Deputy Commissioner Kishtwar Pankaj Kumar Sharma Thursday gave…
DC reviews working of RDD
Calls for timely achievement of targets
GMC gets automatic Gensets to ensure 24×7 power supply
DC inspects facility after commissioning
Kashmir doesn’t need a Switzerland comparison: Shark Tank’s Anupam Mittal
Entrepreneur praises Valley’s raw beauty, affordability
Swadeshi Solar Energy
India is moving towards building solar infrastructure based on Swadesh solar value chain with a focus on indigenous manufacturing…
Sports
MLA Bahu inaugurates dev projects in Nanak Nagar, Sanjay Nagar
Jammu, Sept 11: Member of Legislative assembly (MLA) Bahu Ch Vikram Randhawa…